Fish plays a vital role in the human diet, and consumption per capita is increasing; however, the expansion of industry and agriculture causes contamination of the natural and man-made aquatic environment, which affects the health of organisms, raising safety concerns about its use for human consumption. Consumption of fish products, particularly raw or undercooked fish, is frequently linked to human diseases. As a result, it is critical to research these pathogens in order to ensure the safety of fish. The presence of various bacterial species in fish, including those pathogenic to humans, has been linked to direct contact with contaminated water or feed. Pseudomonas species are bacterial pathogens that infect fish.
 |
| Culture plate showing phage plaques on Pseudomonas bacterial lawn Photo by Hilary kinabo (Student Makerere university) |
Equipment used:
Consumables
Procedures
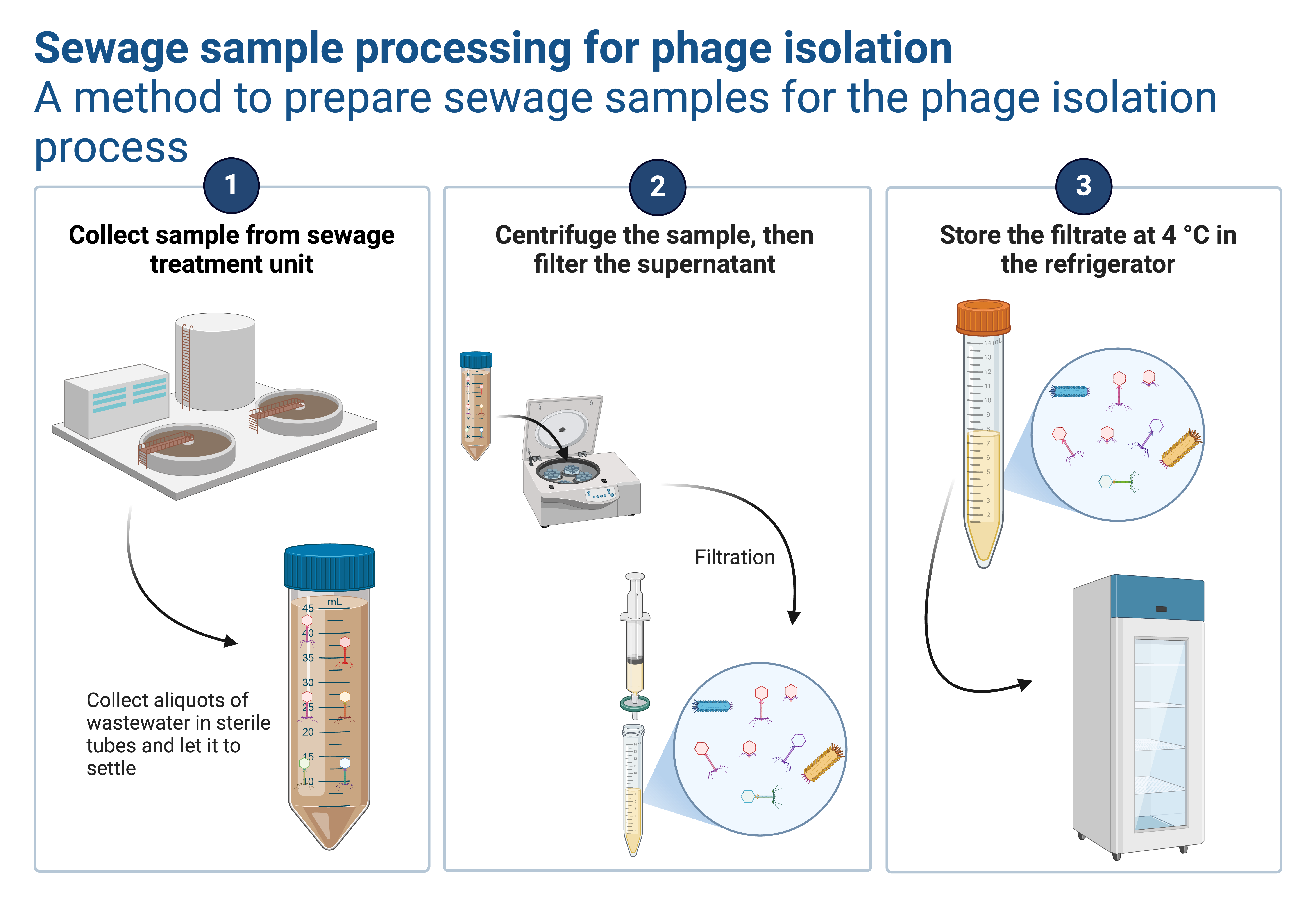
- The fish GIT are obtained and processed into smaller pieces
- The processed samples are then placed into SM buffer, shaken thoroughly, and transferred into the refrigerator at 4°C overnight
- Simultaneously Pseudomonas bacteria (bacteriophage host) pure culture is inoculated in TSB and incubated at 30°C overnight.
- 10ml of the sample in SM buffer is picked and placed in a 15ml falcon tube and centrifuged at 3500 rpm for 10 minutes. The supernatant(assumed to contain phages) is transferred into 50ml falcon tubes and then mixed with the pure culture of pseudomonas bacteria from TSB(10ml) followed by incubation In the incubator shaker for 24 hours. Pure Pseudomonas bacteria is inoculated in TSB overnight.
- After 24 hours if incubation the sample is removed from the incubator shaker and then distributed into falcon tubes (15ml) followed by centrifugation at 3500 rpm for 10 minutes
- The supernatant is placed into the syringe connected to a syringe filter (0.22 nm) and the filtration product will be collected into a clean and sterile falcon tube
- Spot assay will be performed to check for the presence of the Pseudomonas-specific bacteriophages
- 4mls of the LB overlay will be measured and transferred into a clean and sterile falcon tube followed by pipetting 100 μl of the overnight bacterial culture in TSB, the mixture will be mixed well and then immediately poured into the TSA plate forming a Double layer Agar (DLA)
- 10 μl of the sample assumed to contain phages will be measured and spotted into the Double layer agar
- The plate is then placed into the incubator overnight; the residue is autoclaved for proper discarding
- The presence of plaques (zone of clearance) indicates the presence of phages.


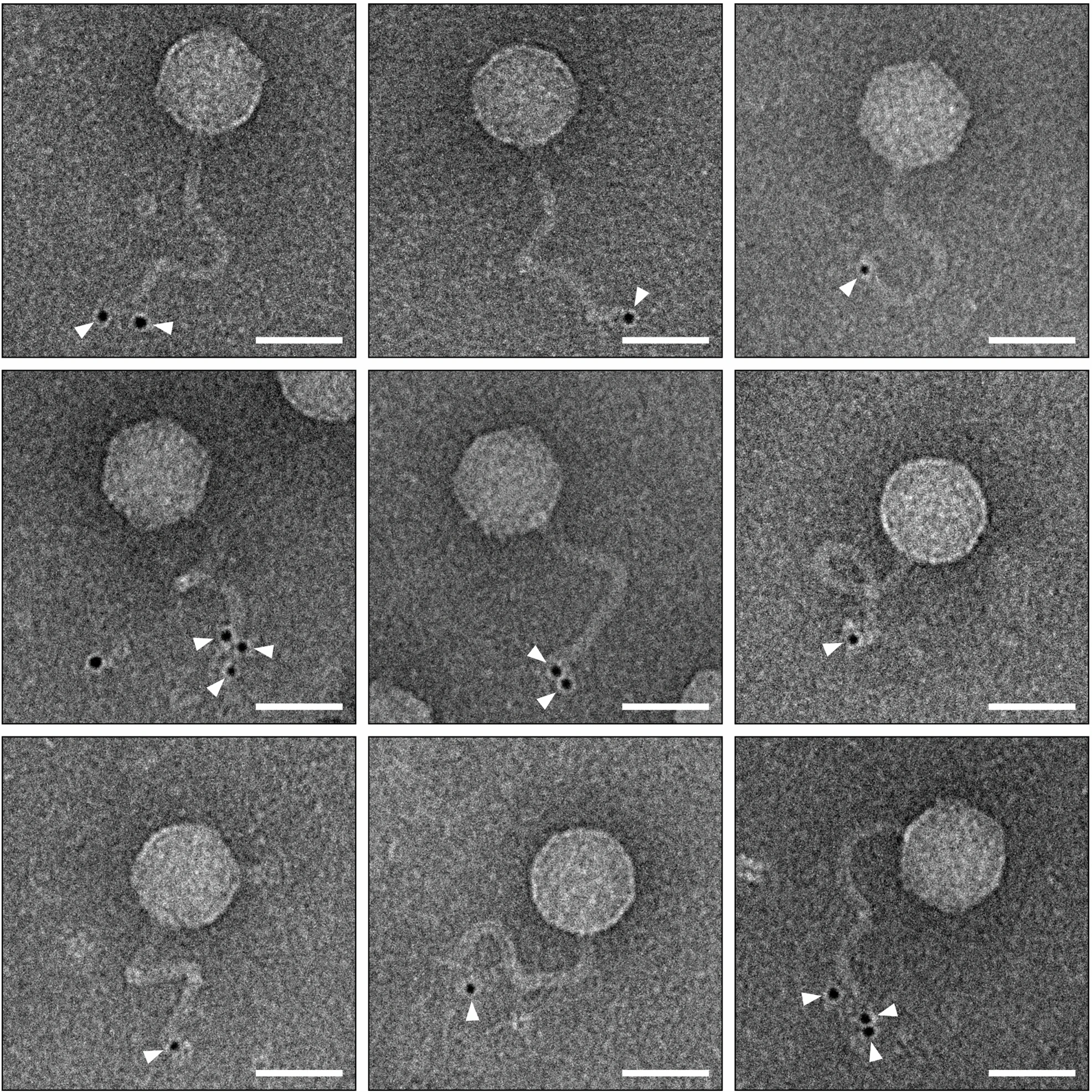

Phages can be utilized in numerous applications to solve challenges facing humanity such as climate change. They could be used to lower the level of methane in the atmosphere.
That is true i agree with you. Im always eager to learn this technology.