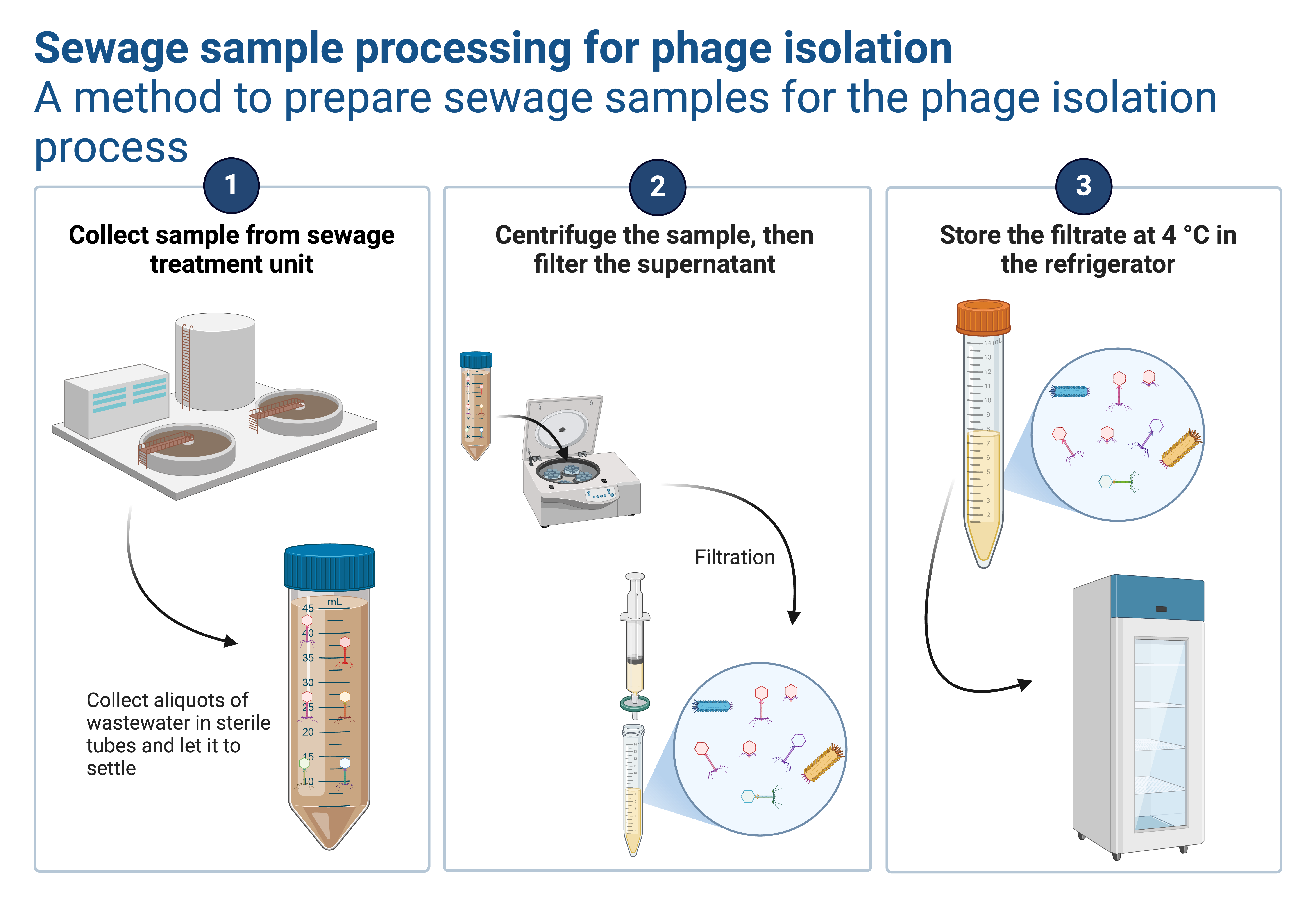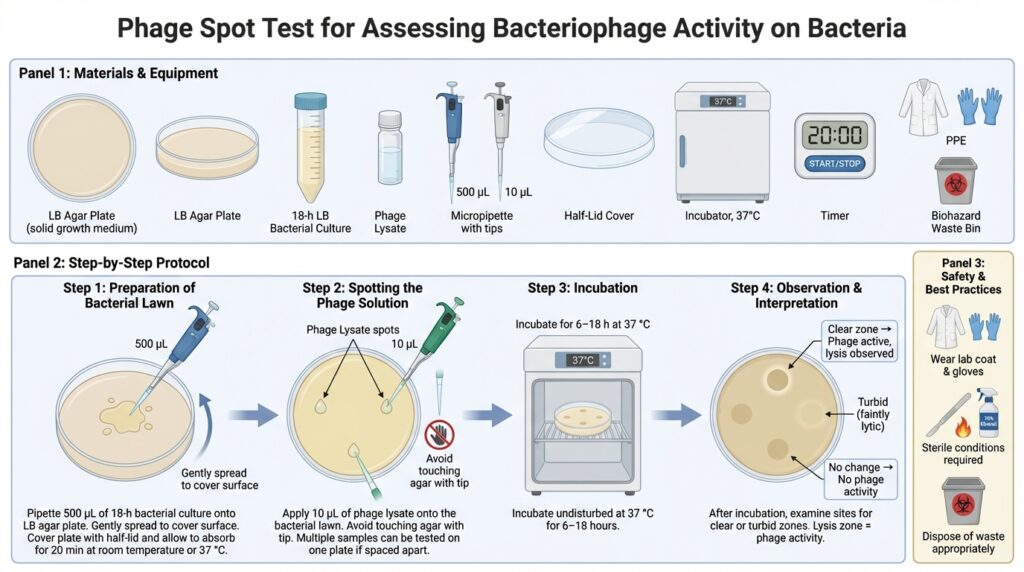
What is a Spot Test?
A spot test is a simple laboratory method used to determine whether a bacteriophage can infect and kill a specific bacterial strain.
In this method, a small volume of a phage solution is placed (“spotted”) onto a bacterial lawn, which is a uniform layer of bacteria grown on an agar plate. During incubation, the phages diffuse into the bacterial layer and interact with the cells.
- If the phages are active, they infect and lyse the bacteria, producing clear zones called plaques or lysis spots.
- If no lysis is observed, the phage is likely inactive against that bacterial strain.
Because it is fast and easy to perform, the spot test is widely used as a qualitative screening tool in phage research and phage therapy to assess host range and phage activity.
Materials Required
Culture Media and Biological Materials
- LB (Luria–Bertani) agar plates
Solid growth medium used to culture bacteria. Plates should be prepared and solidified in advance. - Ready made overlay/soft agar
This will be pored ontop of solid agar. - 18-hour bacterial cultures
Overnight liquid cultures of the target bacterial isolates or reference strains grown in LB broth. - Phage lysate
The bacteriophage sample being tested.
Equipment and Consumables
- Micropipette
Capable of dispensing 500 µL and 10 µL volumes. - Falcon tube
Capable of holding 15 ml. - Sterile pipette tips
Use a new tip for each transfer to avoid contamination. - Half-lid cover
Allows partial airflow while reducing contamination during absorption/you can improvise with a plate lid by partial covering the plate. - Incubator
Set to 37 °C for bacterial growth and phage infection (Temperature may change depending on the bacteria you are dealing with). - Timer or clock
For monitoring incubation times.
Safety Requirements
- Laboratory coat and gloves
- Sterile working conditions
- Proper disposal of biological waste
Note: All media, solutions, and tools should be prepared and sterilized according to standard laboratory procedures before starting the experiment.
Procedure
Step 1: Preparation of the Bacterial Lawn
- If the overlay (soft) agar has solidified, re-melt it by heating and maintain it in a water bath at 45–50 °C.
- Aliquot 4 mL of molten overlay agar into a 15 mL sterile Falcon tube.
- Add 500 µL of an 18-hour LB bacterial culture to the tube containing the molten overlay agar.
- Gently swirl or invert the tube to mix thoroughly, avoiding bubble formation.
- Immediately pour the mixture onto a pre-warmed LB agar plate.
- Gently and quickly tilt the plate to evenly distribute the overlay before it solidifies.
- Leave the plate partially covered with a half-lid.
- Allow the overlay to solidify and absorb for 5–10 minutes at room temperature or 37 °C.
Important:
Bacterial cells are highly active at this stage. To avoid excessive growth and an overly thick lawn, the plate should be used within 1 hour of preparation if kept at room temperature.
- Below ~45 °C → agar may start to solidify too early
- Above ~50 °C → heat stress can kill or injure bacteria, reducing lawn quality
Step 2: Spotting the Phage Solution
- Using a micropipette, carefully place 10 µL of the phage solution onto the surface of the bacterial lawn.
- Avoid touching the agar surface with the pipette tip.
- Multiple phage samples can be tested on the same plate, provided the spots are well separated.
Step 3: Incubation
- Incubate the plates at 37 °C.
- Leave undisturbed for 6–18 hours.
Step 4: Observation and Interpretation
After incubation, examine the plates for clear or turbid zones at the spots where the phage solution was applied.
- Clear plaques or lysis zones
→ Indicates active phage infection and bacterial lysis. - No visible change
→ Suggests the phage does not infect or lyse the tested bacterial strain.
The presence of a lysis zone confirms phage activity against the target bacterium.
Summary
The spot test is a rapid and qualitative method for detecting bacteriophage activity. It is especially useful for:
- Screening phage host range
- Identifying active phages
- Preliminary testing for phage therapy applications