Bacteriophages, for example, provide an alternative mechanism for controlling bacterial diseases in aquaculture. Phage therapy typically entails isolating a variety of bacteriophages specific to a bacterial pathogen that can then be combined as a bacteriophage “cocktail.” Because phages can exhibit strong host specificity, express efficient systems for host cell lysis, and spread rapidly in an aquatic medium, there is growing interest in their use to control fish pathogens in the aquaculture industry. Phage therapy is also unrelated to residues found in aquatic products, which are abundant in nature.
Isolation of bacteriophages from fish gastrointestinal tract samples
Equipment needed;
Consumables;
The procedure of isolating bacteriophages from fish gastrointestinal tract samples;
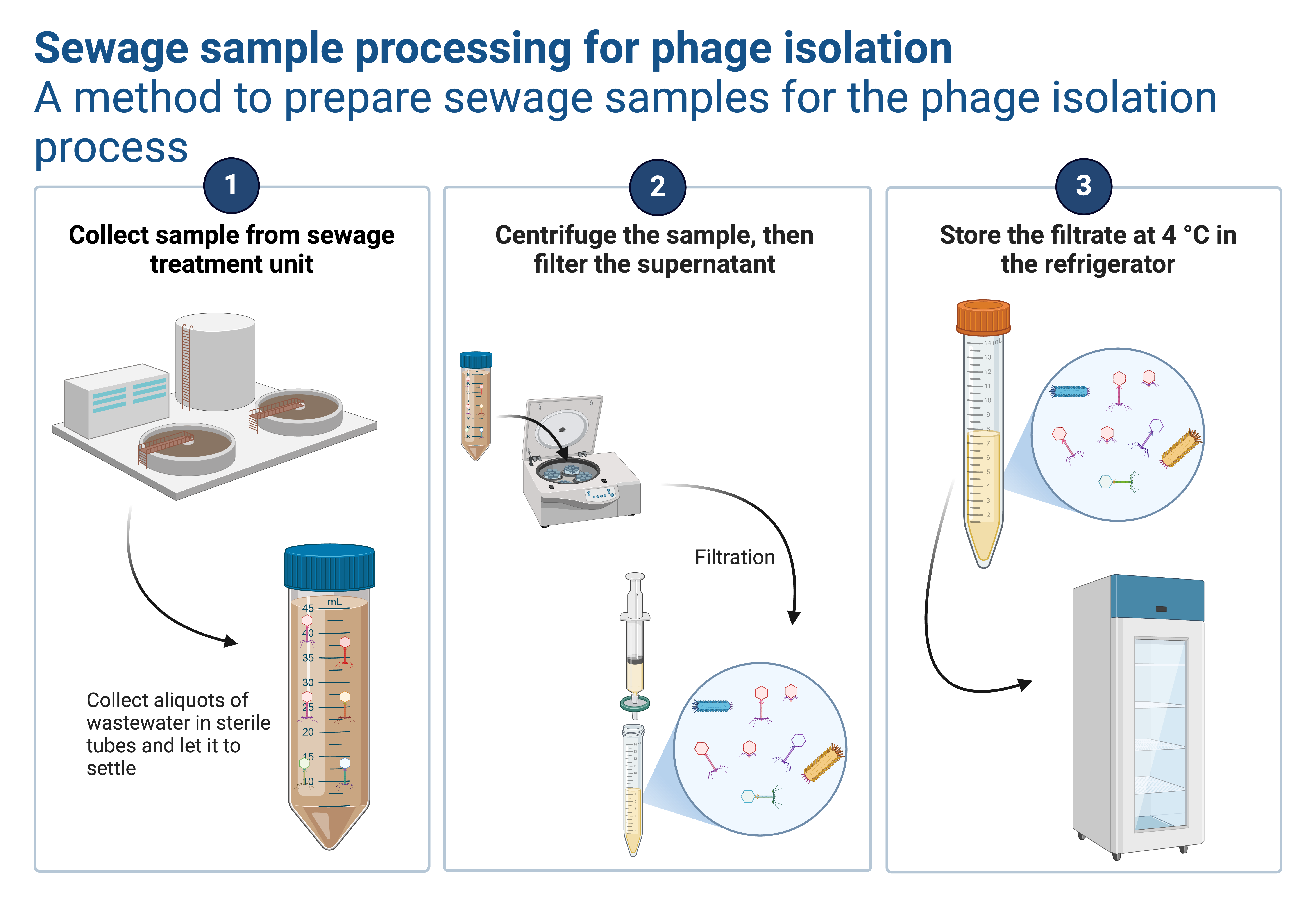
- The fish GIT samples are obtained and chopped into smaller pieces to increase surface area for exposure to their microbial content.
- The processed samples are then placed in SM Buffer, shaken thoroughly, and transferred into the refrigerator overnight (in case not worked on immediately). Meanwhile, the bacteriophage host Edwardsiella sp from 24-hour pure plate culture is inoculated in TSB and incubated overnight.
- A portion of the sample in the SM buffer is obtained into 15ml falcon tubes and then centrifuged at 4000rpm for 15 minutes to remove the coarse particles. The supernatant is transferred into sterile 50ml falcon tubes while the residues are discarded.
- After 24 hours of incubation, the 10mls of the 24-hour TSB bacterial culture is transferred into the 50ml falcon tube mixed with an equal volume of the supernatant obtained from the previous step.
- The 24-hour bacterial-bacteriophage mixture is vortexed and then centrifuged at 4000rpm for 15 minutes.
- The supernatant is then filtered using 0.45nm syringe filters and used for further steps, the residue is discarded by autoclaving.
Spot assay procedure to detect bacteriophages from a lysate
- 100µl of the 24-hour TSB host bacterial culture is pipetted into 4mls of melted overlay agar and mixed well.
- The mixture is then immediately poured over a well-labeled TSA plate and swirled to ensure uniform distribution before solidification.
- This is followed by pipetting 10µl of the filtrate suspected of bacteriophages and spotting on the corresponding label on the TSA plate.
- The above setup is allowed to stand for about 15 minutes to allow diffusion and then transferred into the incubator overnight.
- Plates are then checked for zones of clearance (plaques) and proceeded to the plaque assay.
Possible application of the Isolated Bacteriophages
This guest post was written by
|
|
Ceaser Aluma Anyanzo, Undergraduate student, School biosecurity and laboratory sciences, Makerere university. |


Nice article